How we can help you?
Toshiba’s continuing commitment to new technology allows you to future proof your business with our unique RFID module.
What are the Benefits of RFID?
-
Unique head up function reduces damage to the chips during printing
- Robust validation ensures tags are encoded accurately every time with the following automatic features:
- - Tag validity
- - Retry
- - Encode and verify
- - Faulty tag void print
- - Encode next tag on error
- - Reflected power check
- Faster throughput with Toshiba’s proprietary Short Pitch RFID Encoding Technology (SPRiNT) and Mach 2 RFID data processing
- What special futures support RFID tag usability
- Grey Area detection
- Offset printing (Increase in Speed)
- Head up on chip position
Grey Area Detection
Sometimes a printer encodes tags without problem but gate readers, handy readers or other types of RFID readers fail to read some of these tags.
Cause: the reflected power output of the tag is too low to be detected by the readers over any distance.
What is “Gray area detection”?
The printer measures the reflected power from the tag. If the reflected power is lower than the power required by other readers in the system (i.e. gray area: sometimes writeable, sometimes non-writable), the printer treats those tags as voids and marks them as non-functioning. This will effectively decrease the field error rate in an actual application.
Offset printing
Toshiba’s printer (B-EX4T1) enables the use of short pitch tags Offset Printing. To realize higher through-put for short-pitch labels when producing large batches of labels, the printer first writes data to an RFID tag, then moves the label to the print position and writes the second tag and prints on the first.
Head up on chip position
Head up function (available on the B-EX4T1 if the ribbon save module is fitted) reducing damage to the chips during printing.
Toshiba’s ribbon save technology enables the print head to be raised to allow it to skip the RFID chip contained in the label. This unique function removes the possibility of impact or pressure damage to both the head and the chip. The end result of which is the continued long life of the print head and fewer chip failures after printing.
RFID frequency
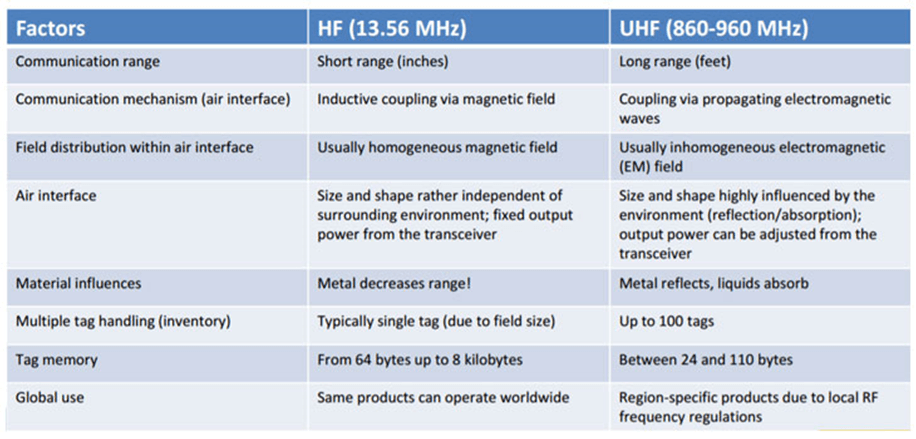
Components in RFID systems



